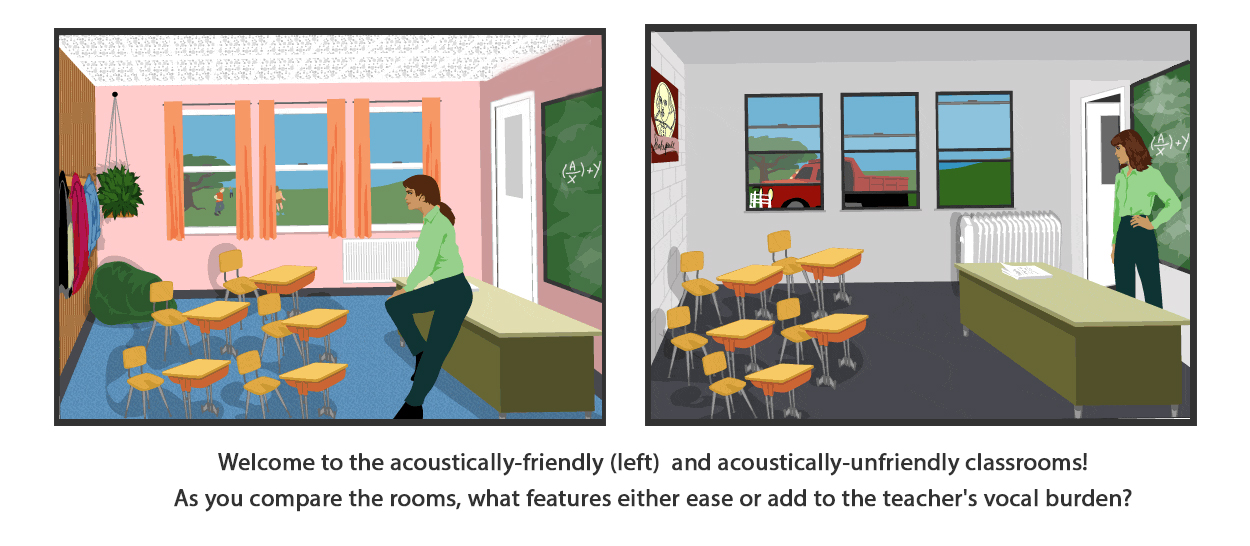
Teacher position: This voice-saving tip doesn't cost a cent, nor does it require physical changes to the classroom. Simply stand closer to your students when you teach. You won't need to crank up your vocal volume to reach your students' ears. In the vocally-unfriendly room, notice the teacher is standing behind her desk, while the students are positioned across the room, near the back wall. This arrangement creates an unnecessarily long distance between the source of sound (the teacher's mouth) and the destination (the students' ears). Unfortunately, this teacher is trying to close the distance gap by raising her vocal volume. Wouldn't it be less vocally fatiguing to merely move closer to the children?
The heating system. An updated, well-functioning and quiet heating and cooling system in the acoustically-friendly classroom can really reduce background ("white") noise. Acoustically friendly heating and cooling systems feature mechanical components located away from "critical listening spaces" (classrooms). In this school, the mechanical equipment is located on the roof above the gymnasium. Adequately-sized ductwork also reduces the speed of air movement and thus, reduces noise. Ideally, an empty classroom should be as quiet as your living room (30-35 decibels). In the less voice friendly classroom, the steam radiator pops, hisses and clanks, adding to the background noise. Heating and air conditioning systems — particularly those in older schools — often feature too-small ducts or inefficient blowers that breed classroom white noise. Although school budgets may not allow for replacement of older systems, it may be possible to improve the size of the ducts or install duct liners.You may also have to consider turning off fans during lectures, and then turning them back on during study periods or small group activities to control temperature.
The windows: The windows — new, thick and tightly-fitted — in the voice-friendly room don't allow clamor from outdoors to seep in. The yips and yells of the kids on the playground are almost completely muffled. The drapes absorb noise. Fabric tends to sop up sound, while unadorned hard window glass bounces sound waves back into the room. However, in the acoustically-unfriendly room, the windows are old with loose frames and thin panes. They are a poor noise barrier between the outdoors and classroom.To make matters worse, a construction site just outside the room has brought a stream of booming trucks. At the very least, the windows should be closed to keep out some offending noise! Also, the classroom has not been outfitted with drapes or shades to deaden reflected sounds. The many hard surfaces in the room create ample opportunities for echoes to develop.
Doors: Does the door in your classroom support your voice? In the voice-friendly room, the door closes tightly to keep out noise from the hall. It does not feature an open transom, and it is located off a small corridor, branched off from a major traffic area. The entrance to the room has two sets of doors, in effect, setting up a "sound lock" buffer. In the less voice-friendly space, the door has been left ajar. Children's voices, slamming lockers, and tennis shoe squeaks from the hallway all pour into the classroom. For this teacher, however, closing the door only resolves part of the noise problem. The door has a hollow core, and it does not fit well in the frame. It's a flimsy defense against the pandemonium in the hallway.
The walls: In the voice-friendly classroom, the wall facing the teacher soaks up sound. To help your students learn, your speech must travel to their ears — but just once. If your speech is reflected back off a hard wall, the echo interferes with your next words. Sorting the echo from the new speech is difficult for your students (particularly those who are hard of hearing or have attention disorders). It also makes your voice compete with itself! Sound-deadening wall coverings are usually soft in texture: fabric panels (such as those found in room dividers) or cork or burlap bulletin boards. A row of hanging sweaters and coats, plants or a beanbag chair will soak up sound. This teacher is also lucky because on the other side of the wall is the school library. In the acoustically-unfriendly classroom, the objects on the wall do nothing to soak up sound. Posters, student papers or chalkboards are not good sound-absorbing materials. When you speak, the sound is reflected. The wall is made of concrete block. Materials such as brick, gypsum board (drywall) and wood paneling are highly reflective, so sounds are bounced around the classroom. A good rule of thumb: the softer the object, the better its sound absorption will be. To add to the problem, the students desks are hugging the rear wall. Unfortunately, the walls of this school were cheaply constructed, and the sound from the adjacent boiler room passes easily through them. The situation could be (slightly) worse: This classroom space could be an "open pod" design, whereby no permanent walls were built at all!
Ceilings: In the voice-friendly room, the low, acoustically tiled ceiling. — while perhaps not aesthetically beautiful — are just about ideal for sound control. Materials used to make the tiles have the ability to absorb about 85 percent of sound striking the surface. The ceiling may be the largest area within the classroom where a single material can be used to absorb — rather than reflect — sound. Thus, the addition of an acoustical tile ceiling can be a real voice-saver for the teacher. When the classroom ceiling soaks up sound, it stops "flutter" echoes. Flutter echoes occur when two large parallel surfaces (such as the ceiling and floor) allow sounds to quickly bounce back and forth, creating a ringing noise. But in the voice-unfriendly classroom, a hard, flat ceiling provides an ideal (and unwelcomed) surface for sounds to reflect. Reflections in the classroom are like echoes in a cave; words repeat over and over. Unlike a visitor to a cave, however, the teacher speaks continuously, and thus, the echoes interfere with the newly spoken words. Ceiling to floor sound waves — or "flutter echoes" — could easily develop in this room. The effect is not unlike a band playing in a school gymnasium, where the acoustics are "live" or "boomy."
Background noise and learning
Research shows that students learn best when their teachers' voices are 10 to 15 dB louder than the background noise in the classroom. (Audiologists would call this a signal to noise ratio.) For younger students particularly, clear messages from their teachers are critical to the learning process. With limited language experience, if children miss even a few of their teachers' words, they are less able to fill in gaps and, thus, get the full message.
The American National Standards Institute recommends 35 dB as the noise level for an empty classroom.
That would mean — under ideal learning conditions — that teachers would speak at 50 dB. Is this a reasonable conversational level? Yes, for many people, but the problem is not yet solved.
Unfortunately, many classrooms are louder than the ANSI 35 dB standard. Heating systems, buzzing lights, noisy children and external noise make the classroom background noise often around 50 dB. Activities — such as group projects — routinely raise the sound level throughout the day. Younger children tend to be noisier than older students. School cafeterias, for example, can get as loud as 80 dB.
Are all sound reflections undesirable?
As you explore the acoustically friendly and acoustically unfriendly classrooms, you might conclude that all sound reflections are detrimental to learning. This is not entirely true, but the acoustics get a little complicated.
In an ideal classroom, the walls and floors would have material to absorb unwanted and reflected sound. The ceiling, however, would feature a hard-surfaced panel to reflect only the teacher's voice to the rear portion of the classroom. The reflective panel would be sloped to further direct the teacher's voice and be composed of a hard material such as plasterboard or plywood. Sound-absorbing material - such as acoustic tile - would surround the reflective panel.
Expensive renovations
| Alterations | Notes |
|---|---|
| Replace window air conditioners with central AC systems | Very expensive to implement |
| Add suspended acoustical tile ceiling | Usually affects lighting as well and may affect ventilation |
| Place fabric wall dividers between tables in the cafeteria | Panels are expensive and create storage issues |
| Replace single-pane windows with well-sealed double-paned windows | |
| Construct walls in place of accordion-style dividers in open style classrooms | |
| Stagger door openings to classrooms (so that they are not adjacent or directly across the hall from one another) |
Medium-priced modifications
| Alterations | Notes |
|---|---|
| Lay an area rug that covers the majority of the hard-surfaced floor (more expensive if wall-to-wall carpet is installed). | Carpets may reduce sound, but create other problems, such as mold or cleanliness issues |
| Install fabric wall panels/burlap bulletin boards | Can pose fire code issues. Code compliant materials could potentially fall in the high-cost category |
| Replace thin or hollow-core doors with solid, tight-fitting doors | |
| Add draperies to windows | May pose fire code issues |
| Add landscaping to the grounds immediately outside of classroom windows | Care needs to be taken to avoid creating indoor air quality problems |
Low-cost solutions
| Alterations | Notes |
|---|---|
| Apply acoustic sealant to gaps between the walls and floors and between the walls and ceiling | Probably will not have notable effects |
| Arrange classroom furniture (breaking up large, open spaces with bookcases, dividers, etc.) | |
| Install hooks so that coats/sweaters are hung on the wall across from where the teacher speaks |